The bones are not joined together firmly at birth. This allows the head to pass through the birth canal. The sutures get minerals added to them over time and harden, firmly joining the skull bones together. This process is called ossification.
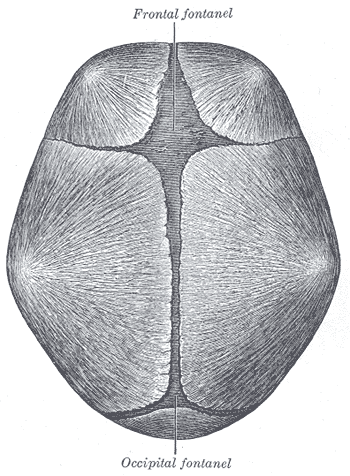
In an infant, the space where two sutures join forms a membrane-covered "soft spot" called a fontanelle (fontanel). The fontanelles allow for growth of the skull during an infant's first year.
There are normally several fontanelles on a newborn's skull, mainly at the top, back, and sides of the head. Like the sutures, fontanelles ossify over time and become closed, solid bony areas. The fontanelle in the back of the head (posterior fontanelle) usually closes by the time an infant is 1 - 2 months old. The fontanelle at the top of the head (anterior fontanelle) usually closes between 7 - 19 months.
The fontanelles should feel firm and very slightly curved inward to the touch. A tense or bulging fontanelle occurs when fluid builds up in the skull cavity or when pressure increases in the brain (increased intracranial pressure).
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Gray198.png
When the infant is crying, lying down, or vomiting, the fontanelles may look like they are bulging, but they should return to normal when the infant is in a calm, head-up position.
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003310.htm
Many animals are born with fonatanelles. These normally close at various points during maturation. During the intervening time the brain is not as well protected as it will be and care should be taken when handling very young animals. Some animals, such as dogs, will have fontanelles that don't close. Which can cause difficulties for the dog (and the dog owner). Pressure on the soft spot can cause brain damage and seizures.
Fun fact - There is no law at the U.S. Federal level prohibiting you from having a human bone in your possession. The fact that some people believe there is or believe there should be such a law is irrelevant.
For more information go to http://www.boneroom.com/faqs/bones.html#bonelaws


No comments:
Post a Comment